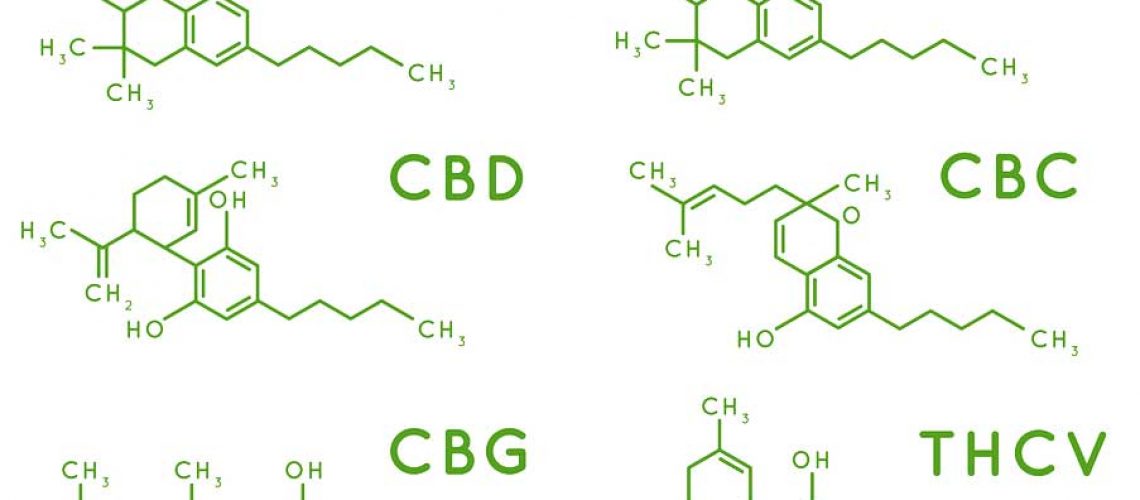
Learn about the different classes of cannabis compounds
What are Phytocannabinoids?
Unlike Endocannabinoids which are produced naturally in our own bodies (and all other land mammals), Phytocannibinoids are produced in plants and are similar in structure which allows them to bond naturally with our endocannabinoid system. According to Dr. Ethan Russoof – GW Pharmaceuticals, “we have studied phytocannabinoids enough to understand that their interaction with terpenoids create an outcome greater than the sum of their parts, a phenomenon he coined the ‘entourage effect'”. Terpenes interact with cannabinoids to alter their effects, often increasing their potency. Because there are over 500 identified compounds in the cannabis plant continued research is needed to catalog the complex effects that these cannabinoids can have on the users experience.
THC
Tetrahydrocannabinol is the most well known of the cannabinoids due to its long term cultural use and its psychoactive and intoxicating use in humans. Its popularity is reinforced also through selective breeding of the black market prior to legalization. THC mostly effects CB1 Receptors and passes the blood brain barrier effecting motor activity, coordination, thinking, appetite, short term memory, pain perception and immune cells. THC primary use medicinally is for its pain relief. Studies have shown that its pain relieving properties exceeds the effect of Advil by twenty times, and twice that of cortisol. Much of the challenge with THC comes with its side effects. Often paranoia or anxiety in certain patients. However, the advent of pairing it with CBD for example may reduce its intoxicating side effects.
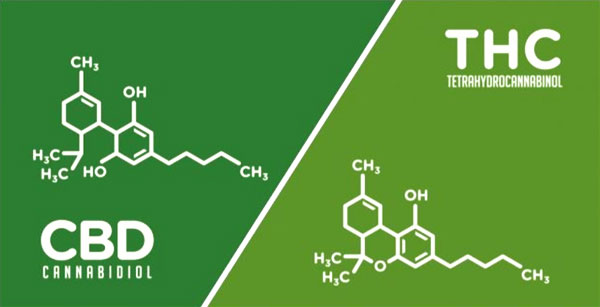
CBD
Cannabidiol is surfacing as the second most popular cannabinoid due to its non intoxicating nature and high concentration in compliant hemp strains.
Other lesser known cannabinoids include CBG, CBN, CBC, CBDV, and THCV. Although these compounds tend to create similar type effects their minute differences in chemical structure create very subtle differences.
What are Terpenes?
Terpenoids from a technical perspective are a class of plant molecules composed from groups of 5-carbon compound base units called isoprene. It is from these isoprene unit combinations which the vast diversity of terpenes are synthesized by the plant. Terpenes are extremely light compounds responsible for the primary odor/scent of many plants. They are so delicate in fact, that they are constantly floating off and away from the plants surface and thus we are able to detect them as an odor.
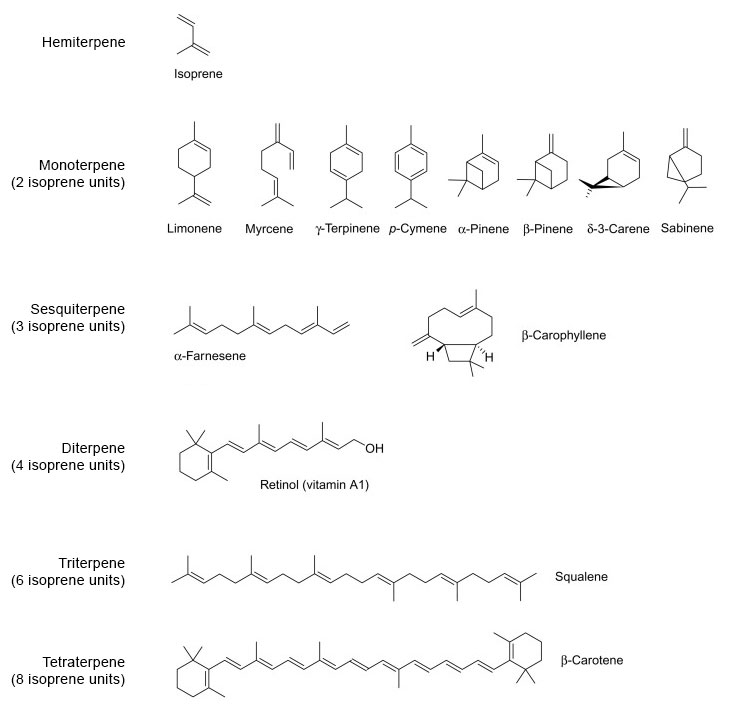
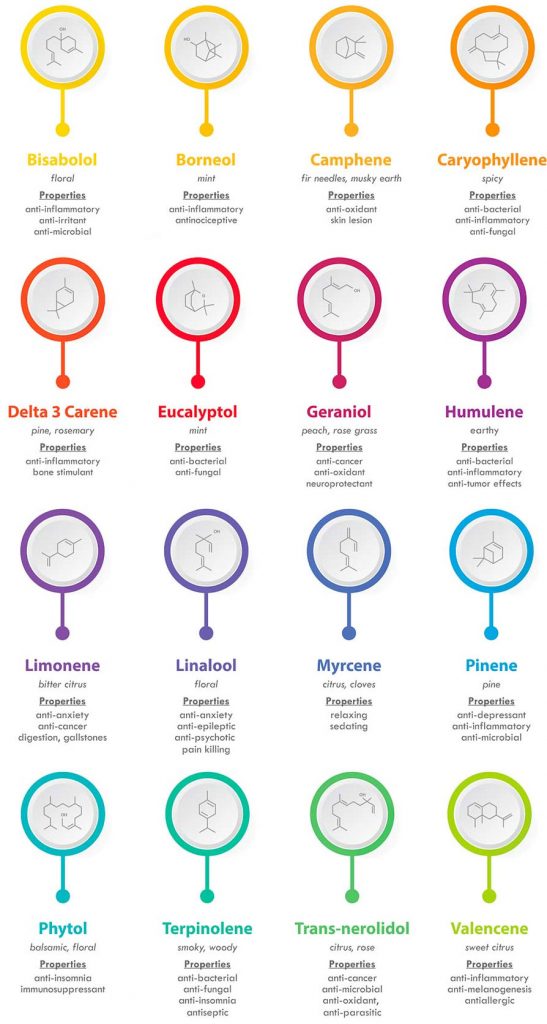
Citrus fruit has high concentrations of Limonene while pine trees contain lots of Pinene. Terpenes and their effects are much more well studied than phytocannabinoids as they are easily observed in plants other than cannabis. Cannabis however displays a wide range of different terpenes in different strains. Some of the more common include; Myrcene, Pinene, Geraniol, Humulene, Linalool, and Limonene. Myrcene is the most commonly known terpene in the cannabis plant. It is said to be responsible for the tranquilizing effect known in Indica dominant strains. It imparts anti-inflammatory and analgesic (pain reliving) qualities and has a very earthy smell and flavor. Myrcene occurs most commonly in mangoes. Alpha and Beta Pinine are the most commonly occurring terpenes on earth. Outside cannabis they can be found in pine trees, orange peels, and herbs like basil and rosemary. Pinene has been shown to be a bronchodilator useful in combating respiratory conditions such as asthma or allergies as it helps open the bronchial pathways in the lungs and nasal cavities. Geraniol is most often associated with floral and fruit smells. Rose oil, Geraniums, Palmarosa, and citronella all contain high concentrations of Geraniol. This terpene boasts antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties and can be used as a pesticide and a bug repellent. Humulene, most prevalent in hops (humulus lupulus) and give beer its bitter, earthy and spicy notes. Studies show that it plays a role in regulating our appetites as well as having antibacterial qualities that may be useful in fighting growth in tumors. Linalool is very common in cannabis and is very pungent. It has been associated with fighting anxiety and depression, and can induce sedative and relaxing sensations. Beyond that it has also been shown to reduce the cognitive impairment and memory loss associated with Alzheimer’s Disease. Limonene is a very appealing scent most common in fresh citrus fruit. It is a common additive to food, candles, and detergents. It has been shown that Limonene plays a roll in regulating our mood and can be uplifting.
Our ethanol extraction process is the most comprehensive and optimal method to recover both the greatest and diverse amount of terpenoids (as well as flavonoids) from the hemp plant. This is why we have a True Full Spectrum CBD Oil that we use for all our products. This isn’t achievable to any significant degree, with CO2, Lipid extraction. You can read our extraction blog here for more information.
What are Flavonoids?
Flavonoids are a class of compounds found in almost all plants that are known to regulate cellular activity and fight free radicals in the body (anti-oxidants). Like terpenes, Flavonoids are not exclusive to cannabis, they also occur naturally in flowers, fruits, and vegetables. However there are specific flavonoids that are only found in cannabis. These are known as cannaflavens. In nature one of the primary functions of flavonoids is pigmentation in plants. Specifically flowers for the purpose of attracting pollinators. It is this quality that gives cannabis its wide variability in color. Purple coloration in cannabis for instance is attributed to anthocyanidins and anthocyanins, which are also found generously in many fruits and vegetables. The orange color of carrots and the red color of tomatoes are attributable to the flavonoids beta-carotene and lycopene respectively.
We often attribute terpenes with creating the distinguishing qualities of cannabis varieties, however flavonoids too play a large part in both odor and flavor. Again, ethanol extraction is the most robust way to procure these compounds safely from the hemp plant, which is why our CBD oil isn’t gold or clear in color. You can read our Full Spectrum vs. Isolate blog here for more information.
References:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4735708/pdf/fpsyg-07-00074.pdf
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273146045_Biomedical_Significance_of_Terpenes_An_Insight
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316495471_Terpenes_from_Forests_and_Human_Health