The benefits of using MCT oil in our CBD products
MCT or Medium-Chain Triglycerides are a fatty acid separated from raw coconut or palm kernel oil using a process called fractionation by simply just applying heat. MCT oil is often used in the health industry for its many benefits, including promoting weight loss, reducing lactic buildup, fighting bacterial and yeast growth, and maintaining blood sugar levels. Some studies suggest that it may even be useful for managing brain function in patients with Epilepsy, Alzheimer’s, and Dementia. Topical applications are also known to produce anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, antioxidant, and skin barrier repair effects. Known as caprylic/capric triglyceride in cosmetics, it’s considered an excellent emollient and skin-replenishing ingredient. It’s included in cosmetics due to its mix of fatty acids that skin can use to replenish its surface and resist moisture loss. Used in CBD products it has many positive effects including increased absorption (bioavailability) and increasing shelf stability.
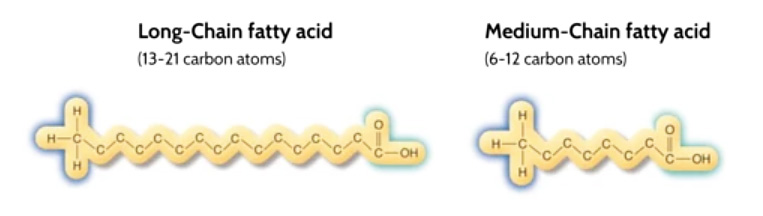
It is important to make the distinction between Medium-Chain Triglycerides and other oils that contain longer chains of molecules. MCT’s contain anywhere from 6-12 carbon molecules attached to glycerol.
Typical cooking oils such as olive, vegetable, and canola oils contain anywhere from 16-20 carbon molecules. Small chain saturated fats such as MCT derived from coconut oil are often labeled as “saturated fats” for labeling purposes but don’t behave like longer chain fatty acids. Medium Chain Fatty Acids (MCFA) are rapidly and efficiently absorbed via the hepatic portal system whereas Longer Chain Fatty Acids (LCFA) are absorbed via the lymphatic system and are therefore less bioavailable.
Increasing the bioavailability and therefore the absorption rate of CBD is essential to creating an effective product. MCTs advantage is providing a healthy oil that is not stored as body fat, but rather burned for energy at the liver or preferentially converted to beneficial ketone bodies, providing sustained energy, glycemic control, weight management, and cognitive benefits. These benefits may be additive or possibly synergistic (greater than the sum of the parts) with CBD. MCTs can increase bioavailability of CBD by increasing solubilization in liquid products and in the gut [3].
The stage of transfer from absorption site in the gut to the bloodstream is critical. The CBD that is able to pass the gastrointestinal barrier is filtered in the liver and then distributed throughout the body where it interacts with the CB1 and CB2 receptors in the body’s endocannabinoid system. Studies show that consuming CBD oil with fatty acids such as MCT’s can help bypass the first phase of metabolism and increases how much CBD is absorbed into the cells during ingestion. Oral bioavailability of CBD on its own is very low (13–19%) [1] due to: limited aqueous solubility. In a study comparing CBD bioavailability in rats it was found that the “co-administration of dietary lipids or pharmaceutical lipid excipients may substantially increase the systemic exposure to orally administered cannabis or cannabis based medicines. Our data suggest that the primary mechanism of the increased absorption of cannabinoids in the presence of lipids is intestinal lymphatic transport.” [2] As shown in the figure below.
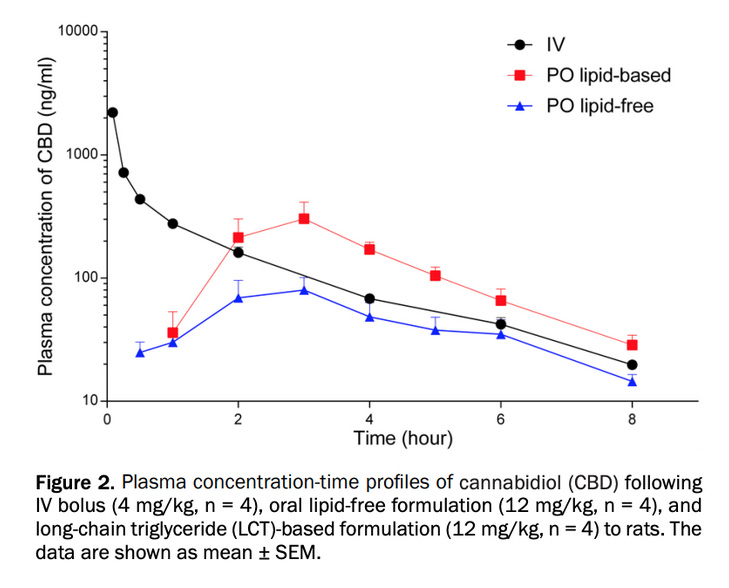
Another practical advantage of solubilizing CBD with MCT oil is the very long shelf life of MCTs, with typical re-test dates being 3 years. Stability is high because there are no double bonds in MCTs to oxidize. Oxidation is a major concern with some vegetable oils and fish oils, imparting bad taste (oils going “rancid”) and undesirable health effects. It is the monoglyceride or fatty acid component of MCTs that are known to have antimicrobial properties [4,5].
Several other factors contribute to the absorption of CBD as well. First is the amount of CBD that is administered. Consuming more CBD leads to a higher concentration in the blood. But only to a point. Saturation levels or a plateauing effect are observed when consuming more than 400mg of CBD. [6]
The second factor that affects absorption is diet. Consuming fatty foods before ingesting CBD may increase bioavailability. One particular study showed that eating a typical breakfast before ingesting CBD resulted in increased absorption. [5].
-
Mechoulam, R., L.A. Parker, and R. Gallily, Cannabidiol: an overview of some pharmacological aspects. J Clin Pharmacol, 2002. 42(S1): p. 11s-19s.
-
Zgair, A., et al., Dietary fats and pharmaceutical lipid excipients increase systemic exposure to orally administered cannabis and cannabis-based medicines. Am J Transl Res, 2016. 8(8): p. 3448-59.
-
Feeney, O.M., et al., 50 years of oral lipid-based formulations: Provenance, progress and future perspectives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2016. 101: p. 167-194.
-
Umerska, A., et al., Antibacterial action of lipid nanocapsules containing fatty acids or monoglycerides as co-surfactants. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 2016. 108: p. 100-110.
-
Berger, A., Coconut Oil – Is it ACTUALLY Good for You? 2019: Amazon Digital Services LLC.
-
Millar, S.A., et al., A systematic review on the pharmacokinetics of cannabidiol in humans. Front. Pharmacol., 2018. 9: p. 1365-1365.
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/mct-oil-benefits
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5796020/pdf/ijms-19-00070.pdf
https://www.paulaschoice.com/ingredient-dictionary/plant-extracts/caprylic%2Fcapric-triglyceride.html






